 |
| April 14, 2015 | Volume 11 Issue 14 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Wheels:
Cadillac CT6 puts heavy focus on mixed-media body structure
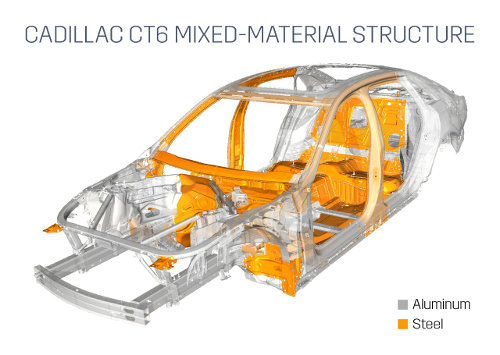
Cadillac will use an advanced mixed-material, aluminum-intensive approach for the lightweight body structure of the CT6 sedan.
Cadillac will use an advanced mixed-material approach for the lightweight body structure of the upcoming CT6 range-topping sedan. The structure is aluminum intensive, but the new Cadillac also includes 13 different materials customized for each area of the car to simultaneously advance driving dynamics, fuel economy, and cabin quietness.
The CT6 debuted March 31 at the New York International Auto Show and will go into production late this year at General Motors' Detroit-Hamtramck assembly plant.
A new body shop with new tooling and advanced technologies -- including 205 robots -- has been added to the plant. The fully automated, roughly 138,000-sq-ft shop is dedicated to the manufacturing of the high-end luxury sedan.
When it launches, the CT6 will expand the Cadillac range upwards -- adding rather than replacing a current product. Positioned above today's CTS and XTS product lines, the CT6 aims to join the elite group of top-class large luxury cars.
"This is the rocket science of automobile construction and manufacturing today," said Cadillac President Johan de Nysschen. "With the CT6, we used high-strength aluminum and high-strength steels -- lightweight chassis components. We integrate aluminum and steel where it makes sense. We eliminate every gram of mass possible, while achieving world-class performance."
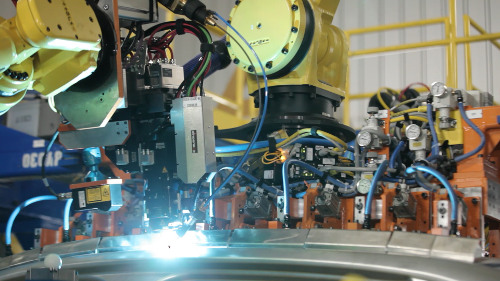
Cadillac will use some of the auto industry's most comprehensive and advanced mixed-material manufacturing techniques to build its all-new top-of-the-line CT6 sedan. Techniques include material joining processes such as aluminum laser welding, shown here.
Weight reduction helps improve fuel efficiency, contributes to desirable vehicle dynamics, and aids in creating a more resilient passenger cell. Sixty-four percent of the CT6 body structure is aluminum, including all exterior body panels -- and the mixed material approach saved 90 kg (198 lb) compared to a predominately steel construction.
Thirteen complex high-pressure die-cast components make up the lower structure of the CT6 body, along with aluminum sheets and extrusions. The vehicle underbody uses steel close-out panels on the lower structure to create a bank vault-quiet cabin without the added weight of extensive sound-deadening material, often used to compensate for aluminum panels in the occupant compartment.
"The structure of the CT6 is one of the most advanced body systems we've ever produced," said Travis Hester, Cadillac CT6 executive chief engineer. "The innovation surrounding our joining techniques has enabled us to create a vehicle structure with the highest torsional rigidity of any Cadillac while achieving one of the most mass-efficient vehicles in the segment."

Cadillac unveiled the new CT6 in New York City on March 31.
Engineers faced a new challenge in manufacturing the advanced mixed-material vehicle structure for the CT6. Combining different types of joining methods, the team overcame previous manufacturing difficulties involving the joining of traditionally dissimilar materials, while still allowing the engineering team to optimize every panel for its desired purpose. Material joining techniques prominent in the body construction of the CT6 include:
- Patented aluminum spot welding technology;
- Aluminum laser welding, which creates a seamless joining of exterior panels;
- Self-piercing rivets, which are able to join different types of materials together with a clean appearance; and
- Flow drill screws, which are able to join different types of materials and are used in conjunction with adhesive.
Aluminum arc welding and structural adhesive are also separately used for CT6 body assembly.
Among the five techniques, the CT6's engineers were able to select the best joining method depending on material combination and body location (for machine equipment access).
To weld both the inner and outer vehicle frames, 28 robots descend on the vehicle body in two separate framing stations, joining the body-in-white together from all angles. The robots are mounted above and beside the vehicle and can also reach beneath it. The two framing processes were choreographed to compensate for different microscopic vibrations, and CT6 body construction resembles an orchestra as the robotic arms move in and out around the vehicle.
Other noteworthy structural-related features include:
- High-strength steel is used strategically to reinforce the body structure, and is also used in conjunction with high-strength aluminum to create a safety cage surrounding the occupants.
- The structural portion of the B-pillar is constructed completely of high-strength steel, which was chosen to aid vehicle ingress, egress, and visibility, in addition to mass savings and added cabin quietness.
- A high-strength aluminum impact bar was added to the rear of the vehicle, and a combination of high-strength aluminum and steel was used for front and side impact zones to further increase passenger safety in the event of collisions.
Once the body construction is complete, a large robotic arm lifts the entire vehicle from one part of the assembly line to an upper-level conveyer -- surprising for a vehicle the size of CT6 -- to be transferred across the Detroit-Hamtramck plant.
Source: Cadillac
Published April 2015
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
